Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Paddle Backend Example: Multi-Graph Matching
This example shows how to match multiple graphs. Multi-graph matching means that more than two graphs are jointly matched.
# Author: Zetian Jiang <maple_jzt@sjtu.edu.cn>
# Ziao Guo <ziao.guo@sjtu.edu.cn>
# Wenzheng Pan <pwz1121@sjtu.edu.cn>
#
# License: Mulan PSL v2 License
Note
The following solvers are included in this example:
rrwm()(classic solver)cao()(classic solver)mgm_floyd()(classic solver)
import os
import time
import math
import copy
import paddle as pd # paddle backend
import itertools
import numpy as np
import pygmtools as pygm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # for plotting
import scipy.io as sio # for loading .mat file
import scipy.spatial as spa # for Delaunay triangulation
from PIL import Image
from matplotlib.patches import ConnectionPatch # for plotting matching result
pygm.set_backend('paddle') # set default backend for pygmtools
Load the images
Images are from the Willow Object Class dataset (this dataset also available with the Benchmark of pygmtools,
see WillowObject).
The images are resized to 256x256.
obj_resize = (256, 256)
n_images = 30
n_outlier = 0
img_list = []
kpts_list = []
n_kpts_list = []
perm_list = []
bm = pygm.benchmark.Benchmark(name='WillowObject',
sets='train',
obj_resize=obj_resize)
while len(img_list) < n_images:
data_list, gt_dict, _ = bm.rand_get_data(cls='Motorbike')
for data in data_list:
img = Image.fromarray(data['img'])
coords = sorted(data['kpts'], key=lambda x: x['labels'])
kpts = pd.to_tensor([[kpt['x'] for kpt in coords],
[kpt['y'] for kpt in coords]])
perm = np.eye(kpts.shape[1])
img_list.append(img)
kpts_list.append(kpts)
n_kpts_list.append(kpts.shape[1])
perm_list.append(perm)
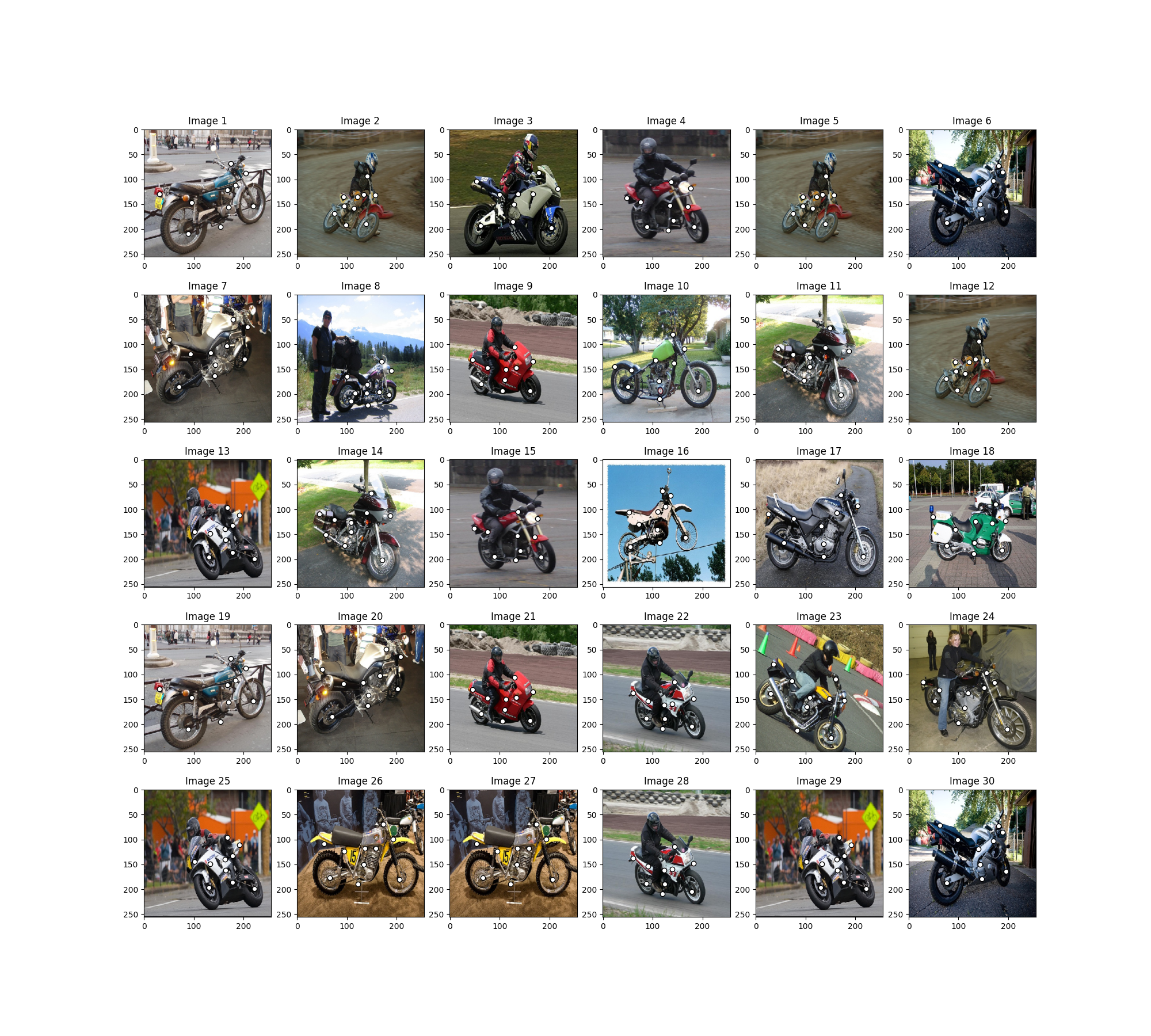
Visualize the images and keypoints
def plot_image_with_graph(img, kpt, A=None):
plt.imshow(img)
plt.scatter(kpt[0], kpt[1], c='w', edgecolors='k')
if A is not None:
for idx in pd.nonzero(A, as_tuple=False):
plt.plot((kpt[0, idx[0]], kpt[0, idx[1]]), (kpt[1, idx[0]], kpt[1, idx[1]]), 'k-')
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 18))
for i in range(n_images):
plt.subplot(5, n_images // 5, i + 1)
plt.title('Image {}'.format(i + 1))
plot_image_with_graph(img_list[i], kpts_list[i])
# plt.savefig('image')
# plt.close()

Build the graphs
Graph structures are built based on the geometric structure of the keypoint set. In this example, we refer to Delaunay triangulation.
def delaunay_triangulation(kpt):
d = spa.Delaunay(kpt.numpy().transpose())
A = pd.zeros((len(kpt[0]), len(kpt[0])))
for simplex in d.simplices:
for pair in itertools.permutations(simplex, 2):
A[pair] = 1
return A
adj_list = []
for i in range(n_images):
A = delaunay_triangulation(kpts_list[i])
adj_list.append(A)
Build affinity matrix
We follow the formulation of Quadratic Assignment Problem (QAP):
where the first step is to build the affinity matrix (\(\mathbf{K}\)) for each pair of graphs
def get_feature(n, points, adj):
"""
:param n: points # of graph
:param points: pd tensor, (n, 2)
:param adj: pd tensor, (n, n)
:return: edge feat, angle feat
"""
points_1 = points.reshape((n, 1, 2)).tile((1, n, 1))
points_2 = points.reshape((1, n, 2)).tile((n, 1, 1))
edge_feat = pd.sqrt(pd.sum((points_1 - points_2) ** 2, axis=2))
edge_feat = edge_feat / pd.max(edge_feat)
angle_feat = pd.atan((points_1[:, :, 1] - points_2[:, :, 1]) / (points_1[:, :, 0] - points_2[:, :, 0] + 1e-8))
angle_feat = 2 * angle_feat / math.pi
return edge_feat, angle_feat
def get_pair_affinity(edge_feat_1, angle_feat_1, edge_feat_2, angle_feat_2, adj1, adj2):
n1, n2 = edge_feat_1.shape[0], edge_feat_2.shape[0]
assert n1 == angle_feat_1.shape[0] and n2 == angle_feat_2.shape[0]
left_adj = adj1.reshape((n1, n1, 1, 1)).tile((1, 1, n2, n2))
right_adj = adj2.reshape((1, 1, n2, n2)).tile((n1, n1, 1, 1))
adj = left_adj * right_adj
left_edge_feat = edge_feat_1.reshape((n1, n1, 1, 1, -1)).tile((1, 1, n2, n2, 1))
right_edge_feat = edge_feat_2.reshape((1, 1, n2, n2, -1)).tile((n1, n1, 1, 1, 1))
edge_weight = pd.sqrt(pd.sum((left_edge_feat - right_edge_feat) ** 2, axis=-1))
left_angle_feat = angle_feat_1.reshape((n1, n1, 1, 1, -1)).tile((1, 1, n2, n2, 1))
right_angle_feat = angle_feat_2.reshape((1, 1, n2, n2, -1)).tile((n1, n1, 1, 1, 1))
angle_weight = pd.sqrt(pd.sum((left_angle_feat - right_angle_feat) ** 2, axis=-1))
affinity = edge_weight * 0.9 + angle_weight * 0.1
affinity = pd.exp(-affinity / 0.1) * adj
affinity = affinity.transpose((0, 2, 1, 3))
return affinity
def generate_affinity_matrix(n_points, points_list, adj_list):
m = len(n_points)
n_max = max(n_points)
affinity = pd.zeros((m, m, n_max, n_max, n_max, n_max))
edge_feat_list = []
angle_feat_list = []
for n, points, adj in zip(n_points, points_list, adj_list):
edge_feat, angle_feat = get_feature(n, points, adj)
edge_feat_list.append(edge_feat)
angle_feat_list.append(angle_feat)
for i, j in itertools.product(range(m), range(m)):
pair_affinity = get_pair_affinity(edge_feat_list[i],
angle_feat_list[i],
edge_feat_list[j],
angle_feat_list[j],
adj_list[i],
adj_list[j])
affinity[i, j] = pd.cast(pair_affinity, 'float32')
affinity = affinity.transpose((0, 1, 3, 2, 5, 4)).reshape((m, m, n_max * n_max, n_max * n_max))
return affinity
affinity_mat = generate_affinity_matrix(n_kpts_list, kpts_list, adj_list)
m = len(kpts_list)
n = int(pd.max(pd.to_tensor(n_kpts_list)))
ns_src = pd.ones(m * m, dtype=pd.int32) * n
ns_tgt = pd.ones(m * m, dtype=pd.int32) * n
Calculate accuracy, consistency, and affinity
def cal_accuracy(mat, gt_mat, n):
m = mat.shape[0]
acc = 0
for i in range(m):
for j in range(m):
_mat, _gt_mat = mat[i, j], gt_mat[i, j]
row_sum = pd.sum(_gt_mat, axis=0)
col_sum = pd.sum(_gt_mat, axis=1)
row_idx = [k for k in range(n) if row_sum[k] != 0]
col_idx = [k for k in range(n) if col_sum[k] != 0]
# print(row_idx)
_mat = pd.index_select(_mat, pd.to_tensor(row_idx), axis=0)
_mat = pd.index_select(_mat, pd.to_tensor(col_idx), axis=1)
_gt_mat = pd.index_select(_gt_mat, pd.to_tensor(row_idx), axis=0)
_gt_mat = pd.index_select(_gt_mat, pd.to_tensor(col_idx), axis=1)
acc += 1 - pd.sum(pd.abs(_mat - _gt_mat)) / 2 / (n - n_outlier)
return acc / (m * m)
def cal_consistency(mat, gt_mat, m, n):
return pd.mean(get_batch_pc_opt(mat))
def cal_affinity(X, X_gt, K, m, n):
X_batch = X.reshape((-1, n, n))
X_gt_batch = X_gt.reshape((-1, n, n))
K_batch = K.reshape((-1, n * n, n * n))
affinity = get_batch_affinity(X_batch, K_batch)
affinity_gt = get_batch_affinity(X_gt_batch, K_batch)
return pd.mean(affinity / (affinity_gt + 1e-8))
def get_batch_affinity(X, K, norm=1):
"""
calculate affinity score
:param X: (b, n, n)
:param K: (b, n*n, n*n)
:param norm: normalization term
:return: affinity_score (b, 1, 1)
"""
b, n, _ = X.shape
vx = X.transpose((0, 2, 1)).reshape((b, -1, 1)) # (b, n*n, 1)
vxt = vx.transpose((0, 2, 1)) # (b, 1, n*n)
affinity = pd.bmm(pd.bmm(vxt, K), vx) / norm
return affinity
def get_single_affinity(X, K, norm=1):
"""
calculate affinity score
:param X: (n, n)
:param K: (n*n, n*n)
:param norm: normalization term
:return: affinity_score scale
"""
n, _ = X.shape
vx = X.transpose((0, 1)).reshape((-1, 1))
vxt = vx.transpose((0, 1))
affinity = pd.matmul(pd.matmul(vxt, K), vx) / norm
return affinity
def get_single_pc(X, i, j, Xij=None):
"""
:param X: (m, m, n, n) all the matching results
:param i: index
:param j: index
:param Xij: (n, n) matching
:return: the consistency of X_ij
"""
m, _, n, _ = X.shape
if Xij is None:
Xij = X[i, j]
pair_con = 0
for k in range(m):
X_combo = pd.matmul(X[i, k], X[k, j])
pair_con += pd.sum(pd.abs(Xij - X_combo)) / (2 * n)
return 1 - pair_con / m
def get_single_pc_opt(X, i, j, Xij=None):
"""
:param X: (m, m, n, n) all the matching results
:param i: index
:param j: index
:return: the consistency of X_ij
"""
m, _, n, _ = X.shape
if Xij is None:
Xij = X[i, j]
X1 = X[i, :].reshape((-1, n, n))
X2 = X[:, j].reshape((-1, n, n))
X_combo = pd.bmm(X1, X2)
pair_con = 1 - pd.sum(pd.abs(Xij - X_combo)) / (2 * n * m)
return pair_con
def get_batch_pc(X):
"""
:param X: (m, m, n, n) all the matching results
:return: (m, m) the consistency of X
"""
pair_con = pd.zeros((m, m))
for i in range(m):
for j in range(m):
pair_con[i, j] = get_single_pc_opt(X, i, j)
return pair_con
def get_batch_pc_opt(X):
"""
:param X: (m, m, n, n) all the matching results
:return: (m, m) the consistency of X
"""
m, _, n, _ = X.shape
X1 = X.reshape((m, 1, m, n, n)).tile((1, m, 1, 1, 1)).reshape((-1, n, n)) # X1[i, j, k] = X[i, k]
X2 = X.reshape((1, m, m, n, n)).tile((m, 1, 1, 1, 1)).transpose((0, 2, 1, 3, 4)).reshape((-1, n, n)) # X2[i, j, k] = X[k, j]
X_combo = pd.bmm(X1, X2).reshape((m, m, m, n, n))
X_ori = X.reshape((m, m, 1, n, n)).tile((1, 1, m, 1, 1))
pair_con = 1 - pd.sum(pd.abs(X_combo - X_ori), axis=(2, 3, 4)) / (2 * n * m)
return pair_con
def eval(mat, gt_mat, affinity, m, n):
acc = cal_accuracy(mat, gt_mat, n)
src = cal_affinity(mat, gt_mat, affinity, m, n)
con = cal_consistency(mat, gt_mat, m, n)
return acc, src, con
Generate gt mat
gt_mat = pd.zeros((m, m, n, n))
for i in range(m):
for j in range(m):
gt_mat[i, j] = pd.to_tensor(np.matmul(perm_list[i].transpose((0, 1)), perm_list[j]), dtype='float32')
# print(perm_list[0])
# print(perm_list[1])
# print(gt_mat[1, 2])
# print(gt_mat[0, 1] - gt_mat[1, 0].transpose(0, 1))
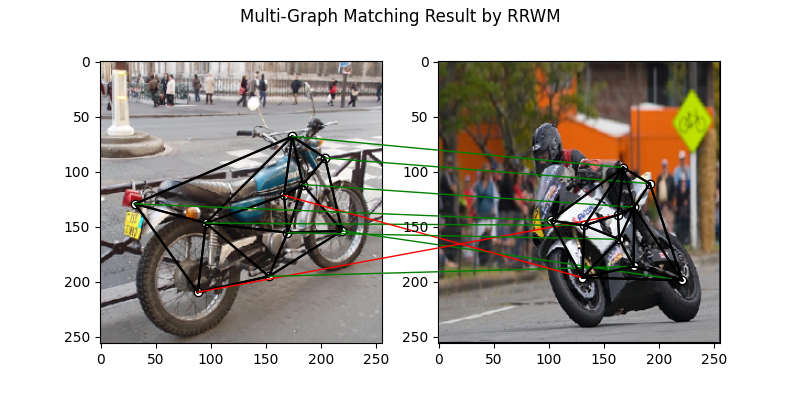
Pairwise graph matching by RRWM
See rrwm() for the API reference.
a = 0
b = 12
tic = time.time()
rrwm_mat = pygm.classic_solvers.rrwm(affinity_mat.reshape((-1, n * n, n * n)), ns_src, ns_tgt)
rrwm_mat = pygm.linear_solvers.hungarian(rrwm_mat)
toc = time.time()
rrwm_mat = rrwm_mat.reshape((m, m, n, n))
rrwm_acc, rrwm_src, rrwm_con = eval(rrwm_mat, gt_mat, affinity_mat, m, n)
rrwm_tim = toc - tic
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
plt.suptitle('Multi-Graph Matching Result by RRWM')
ax1 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plot_image_with_graph(img_list[a], kpts_list[a], adj_list[a])
ax2 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plot_image_with_graph(img_list[b], kpts_list[b], adj_list[b])
X = rrwm_mat[a, b]
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
j = pd.argmax(X[i]).item()
con = ConnectionPatch(xyA=kpts_list[a][:, i], xyB=kpts_list[b][:, j], coordsA="data", coordsB="data",
axesA=ax1, axesB=ax2, color="red" if i != j else "green")
plt.gca().add_artist(con)
# plt.savefig("RRWM.png")
# plt.close()
/home/wzever/miniconda3/envs/pygmtools/lib/python3.10/site-packages/paddle/fluid/variable_index.py:292: UserWarning: 1-D Tensor will be treat as advanced indexing in future version. Currently, 1-D Tensor means a scalar, not vector, and please modify it to 0-D Tensor. If advanced indexing is needed, please use `export FLAGS_set_to_1d=False` to set the flag.
warnings.warn(
/home/wzever/miniconda3/envs/pygmtools/lib/python3.10/site-packages/paddle/fluid/variable_index.py:591: UserWarning: Warning: In Tensor '__getitem__', if the number of scalar elements in the index is equal to the rank of the Tensor, the output should be 0-D. In order to be consistent with the behavior of previous versions, it will be processed to 1-D. But it is not correct and will be removed in release 2.6. If 1-D is still wanted, please modify the index element from scalar to slice (e.g. 'x[i]' => 'x[i:i+1]').
warnings.warn(
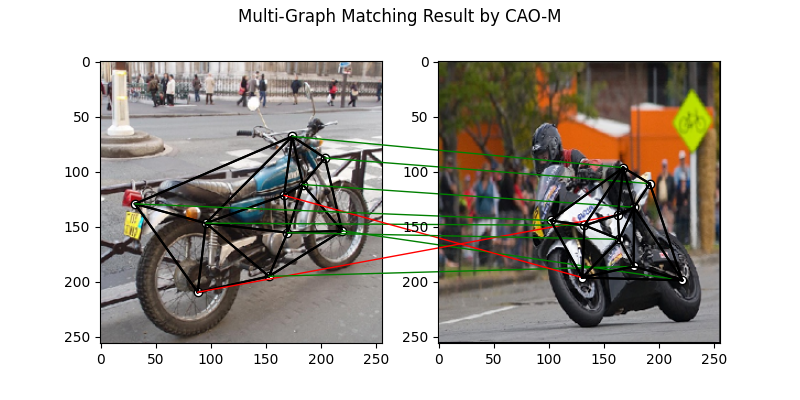
Multi graph matching by multi-graph solvers
Multi graph matching: CAO-M See
cao()for the API reference.
base_mat = copy.deepcopy(rrwm_mat)
tic = time.time()
cao_m_mat = pygm.multi_graph_solvers.cao(affinity_mat, base_mat, mode='memory')
cao_m_mat = pygm.linear_solvers.hungarian(cao_m_mat.reshape((-1, n, n))).reshape((m, m, n, n))
toc = time.time()
cao_m_acc, cao_m_src, cao_m_con = eval(cao_m_mat, gt_mat, affinity_mat, m, n)
cao_m_tim = toc - tic + rrwm_tim
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
plt.suptitle('Multi-Graph Matching Result by CAO-M')
ax1 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plot_image_with_graph(img_list[a], kpts_list[a], adj_list[a])
ax2 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plot_image_with_graph(img_list[b], kpts_list[b], adj_list[b])
X = cao_m_mat[a, b]
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
j = pd.argmax(X[i]).item()
con = ConnectionPatch(xyA=kpts_list[a][:, i], xyB=kpts_list[b][:, j], coordsA="data", coordsB="data",
axesA=ax1, axesB=ax2, color="red" if i != j else "green")
plt.gca().add_artist(con)
# plt.savefig("CAO-M.png")
# plt.close()
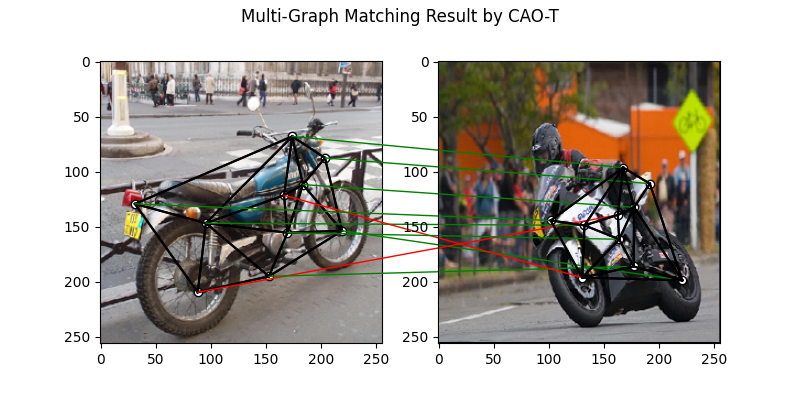
Multi graph matching: CAO-T
See cao() for the API reference.
base_mat = copy.deepcopy(rrwm_mat)
tic = time.time()
cao_t_mat = pygm.multi_graph_solvers.cao(affinity_mat, base_mat, mode='time')
cao_t_mat = pygm.linear_solvers.hungarian(cao_t_mat.reshape((-1, n, n))).reshape((m, m, n, n))
toc = time.time()
cao_t_acc, cao_t_src, cao_t_con = eval(cao_t_mat, gt_mat, affinity_mat, m, n)
cao_t_tim = toc - tic + rrwm_tim
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
plt.suptitle('Multi-Graph Matching Result by CAO-T')
ax1 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plot_image_with_graph(img_list[a], kpts_list[a], adj_list[a])
ax2 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plot_image_with_graph(img_list[b], kpts_list[b], adj_list[b])
X = cao_t_mat[a, b]
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
j = pd.argmax(X[i]).item()
con = ConnectionPatch(xyA=kpts_list[a][:, i], xyB=kpts_list[b][:, j], coordsA="data", coordsB="data",
axesA=ax1, axesB=ax2, color="red" if i != j else "green")
plt.gca().add_artist(con)
# plt.savefig("CAO-T.png")
# plt.close()
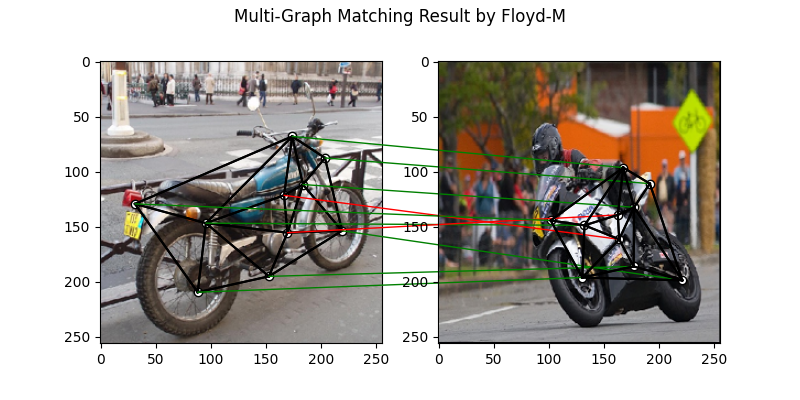
Multi graph matching: MGM-Floyd-M
See mgm_floyd() for the API reference.
base_mat = copy.deepcopy(rrwm_mat)
tic = time.time()
floyd_m_mat = pygm.multi_graph_solvers.mgm_floyd(affinity_mat, base_mat, param_lambda=0.4, mode='memory')
floyd_m_mat = pygm.linear_solvers.hungarian(floyd_m_mat.reshape((-1, n, n))).reshape((m, m, n, n))
toc = time.time()
floyd_m_acc, floyd_m_src, floyd_m_con = eval(floyd_m_mat, gt_mat, affinity_mat, m, n)
floyd_m_tim = toc - tic + rrwm_tim
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
plt.suptitle('Multi-Graph Matching Result by Floyd-M')
ax1 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plot_image_with_graph(img_list[a], kpts_list[a], adj_list[a])
ax2 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plot_image_with_graph(img_list[b], kpts_list[b], adj_list[b])
X = floyd_m_mat[a, b]
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
j = pd.argmax(X[i]).item()
con = ConnectionPatch(xyA=kpts_list[a][:, i], xyB=kpts_list[b][:, j], coordsA="data", coordsB="data",
axesA=ax1, axesB=ax2, color="red" if i != j else "green")
plt.gca().add_artist(con)
# plt.savefig("Floyd-M.png")
# plt.close()
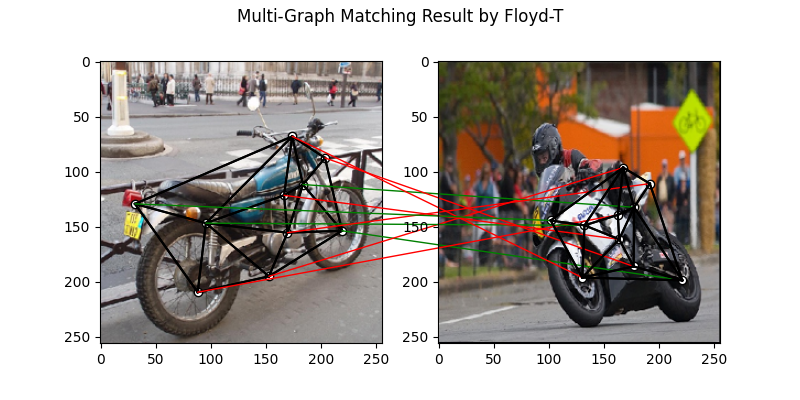
Multi graph matching: MGM-Floyd-T
See mgm_floyd() for the API reference.
base_mat = copy.deepcopy(rrwm_mat)
tic = time.time()
floyd_t_mat = pygm.multi_graph_solvers.mgm_floyd(affinity_mat, base_mat, param_lambda=0.6, mode='time')
floyd_t_mat = pygm.linear_solvers.hungarian(floyd_t_mat.reshape((-1, n, n))).reshape((m, m, n, n))
toc = time.time()
floyd_t_acc, floyd_t_src, floyd_t_con = eval(floyd_t_mat, gt_mat, affinity_mat, m, n)
floyd_t_tim = toc - tic + rrwm_tim
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 4))
plt.suptitle('Multi-Graph Matching Result by Floyd-T')
ax1 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plot_image_with_graph(img_list[a], kpts_list[a], adj_list[a])
ax2 = plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plot_image_with_graph(img_list[b], kpts_list[b], adj_list[b])
X = floyd_t_mat[a, b]
for i in range(X.shape[0]):
j = pd.argmax(X[i]).item()
con = ConnectionPatch(xyA=kpts_list[a][:, i], xyB=kpts_list[b][:, j], coordsA="data", coordsB="data",
axesA=ax1, axesB=ax2, color="red" if i != j else "green")
plt.gca().add_artist(con)
# plt.savefig("Floyd-T.png")
# plt.close()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 46.850 seconds)